Overview
This portfolio serves to document my contributions in a team-based software engineering project for the module CS2113T. The team comprises of 4 members ad we were tasked to develop a working application within 8 weeks. We decided to morph the existing application into a task manager, called Student Buddy.
To comply with the module requirements, the team is constrained to start from an existing code base – Address Book Level 4 and the user must interact with the application via Command Line interface(CLI).
Student Buddy is a desktop application created for students to assist them in managing their schedule.
Summary of contributions
This section shows a summary of my coding, documentation, and other helpful contributions to Student Buddy.
-
Major enhancement: added the ability to
sorttasks-
What it does: It allows the user to sort the tasks in the task list based on name, module code, date due or priority level.
-
Justification: This feature improves significantly because it allows the user to organise the task list in a manner of their choosing.
-
Highlights: It required an in-depth analysis and understanding on how the different components of the task manager is involved with each other.
-
-
Minor enhancement: refactored the existing Address Book Level 4 and edited the code to make a basic task manager that was used as the base of Student Buddy.
-
Minor enhancement: created a
daysRemainingfunction to find number of days remaining till the task is due and gave colour codes depending on how much days are left. -
Minor enhancement: created
findname,findmodule,finddateandfindprioritycommands to be able to search not only by task name but by other variables. -
Code contributed: Reposense
-
Other contributions:
-
Project management:
-
Set up the organization repository and its issue tracker
-
Managed releases
v1.2andv1.3on GitHub
-
-
Enhancement to existing features:
-
Documentation:
-
Community:
-
Contributions to the User Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the User Guide. They showcase my ability to write documentation targeting end-users with the aim of providing clear and concise instructions at a level that is easy for the end-user to follow. |
(Start of extract from the User Guide)
Locating tasks by name: findname, fn
Finds tasks with names containing any of the given keywords.
Format: findname KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] or fn KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Examples:
-
findname Project Tutorial
Returns all task with names containingProjectorTutorial. -
fn Project Lab Report
Returns all task having namesProject,Lab, orReport
Locating tasks by module code: findmodule, fm
Finds tasks with module codes containing any of the given keywords.
Format: findmodule KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] or fm KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Examples:
-
findmodule CS2113T
Returns all tasks containing the module codeCS2113T. -
fm CS2113T CS2101
Returns all tasks containing the module codeCS2113TorCS2101.
Locating tasks by date: finddate, fd
Finds tasks with dates containing any of the given keywords.
Format: finddate KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] or fd KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Examples:
-
finddate 20-03
Returns all task with date 20-03. -
fd 20-03 30-03
Returns all task with date 20-03 or 30-03.
Locating tasks by priority code: findpriority, fp
Finds tasks with priority code containing any of the given keywords.
Format: findpriority KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] or fp KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Examples:
-
findpriority 1
Returns all task with priority code 1. -
fp 1 3
Returns all task with priority code 1 or 3.
Sorting the task list : sort, s
Sorts the task list in Student Buddy according to an input parameter.
Format: sort PARAMETER or s PARAMETER
Examples:
-
sort module
Sorts the task list lexicographically by module code. -
s priority
Sorts the task list in descending order by priority. -
s d
Sorts the task list in chronological order by date
Deleting Overdue Tasks : deleteoverdue, delod [coming in v2.0]
Deletes all tasks that are overdue.
Format: deleteoverdue or delod
Examples:
-
list
deleteoverdue
Deletes all the overdue tasks in Student Buddy. -
findname Project
delod
Deletes all the task in the results of thefindnamecommand.
(End of extract)
Contributions to the Developer Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the Developer Guide. They showcase my ability to write technical documentation and the technical depth of my contributions to the project. |
(Start of extract from the Developer Guide)
Task Feature
Current Implementation
The task list is created by refactoring the existing code in the Address Book Level 4
The class diagram below illustrates the task class.

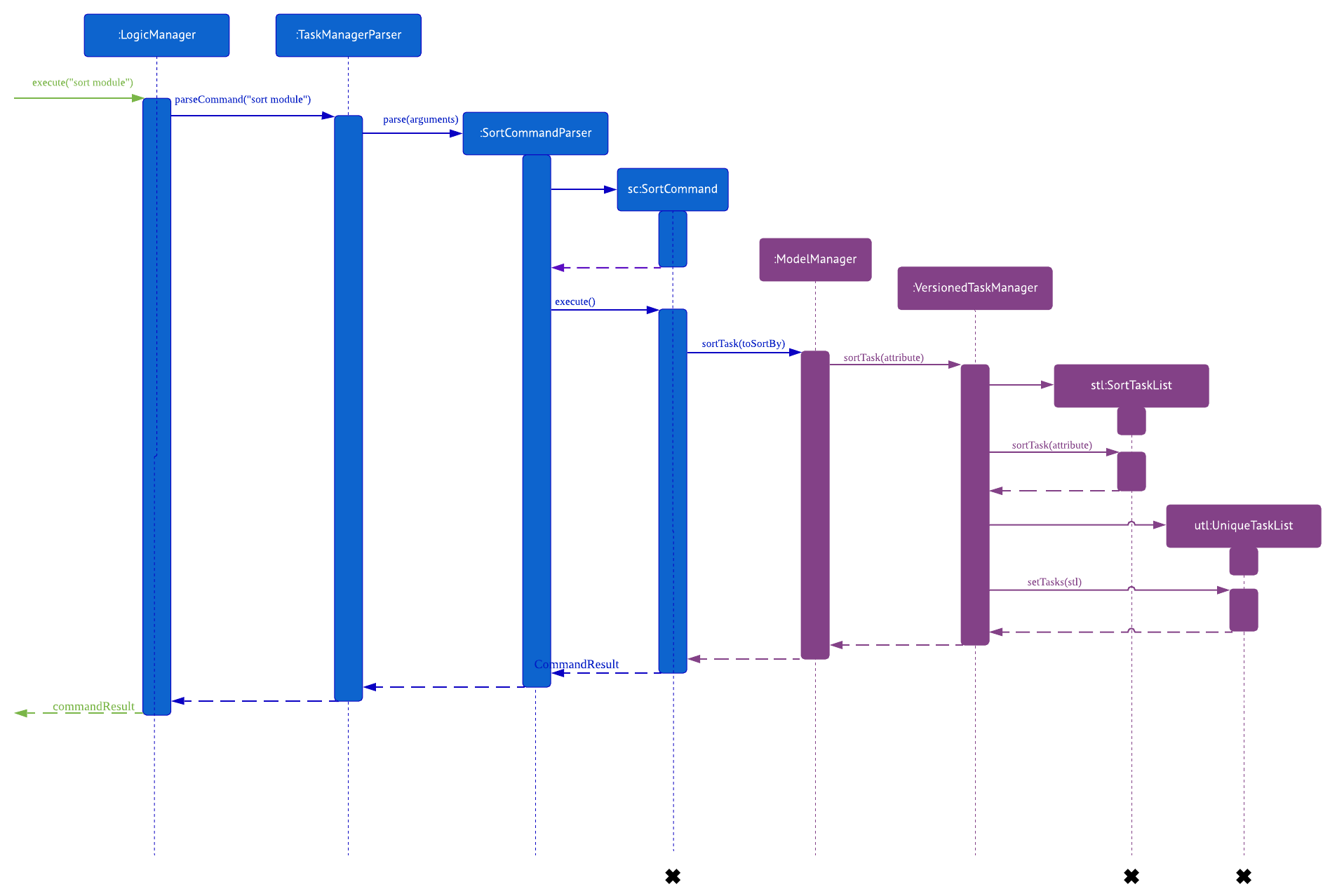
Sort Task List Feature
Current Implementation
The sorting mechanism is facilitated by TaskManager, Model and SortTaskList.
Given below is an example usage scenario.
Step 1. The user keys in |
Step 2. If the attribute is valid, it will then create a new |
Step 3. |
Step 4. It will then call |
Step 5. Then, we use |
The Sequence Diagram below illustrates how the sort mechanism functions. More specifically, sorting by module code.
Design Considerations
Aspect: How sort executes
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Write a class separately for handling the sorting of the task list.
-
Pros: Easy to read and debug, Follows OOP coding and thus easier for other coders to modify.
-
Cons: Difficult to implement.
-
-
Alternative 2: Write a method for each attribute in
TaskManager.-
Pros: Easy to implement.
-
Cons: Does not follow OOP coding.
-
[Proposed] Delete overdue
Proposed Implementation
Using the existing daysRemaining variable, upon entering DeleteOverdue in the command line, the command will iterate through all the tasks and check the value of daysRemaining.
If it is less than 0, the command will call the DeleteCommand to delete the overdue task.
Aspect: How the delete overdue command executes
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Write the command such that whenever there is an overdue task, it will call the
deletecommand.-
Pros: Easy to use as it does not require changing the existing code much.
-
Cons: Will need to iterate through all the tasks.
-
-
Alternative 2: Create a new class to store all overdue tasks that updates itself whenever a task is overdue.
-
Pros: Faster as it does not require iterating through all tasks.
-
Cons: Requires more space to store all the overdue tasks
-
Use Cases
Use case: Find task by name
MSS
-
User requests to find a task by name
-
Student Buddy shows the tasks according to user’s input
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty
Use case ends.
-
2b. The given index is invalid
-
2bi. Student Buddy returns an error
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Find task by module
MSS
-
User requests to find a task by module
-
Student Buddy shows the tasks according to user’s input
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty
Use case ends.
-
2b. The given index is invalid
-
2bi. Student Buddy returns an error
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Find task by date
MSS
-
User requests to find a task by date
-
Student Buddy shows the tasks according to user’s input
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty
Use case ends.
-
2b. The given index is invalid
-
2bi. Student Buddy returns an error
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Find task by priority
MSS
-
User requests to find a task by priority
-
Student Buddy shows the tasks according to user’s input
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty
Use case ends.
-
2b. The given index is invalid
-
2bi. Student Buddy returns an error
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Sort tasks
MSS
-
User requests to sort tasks by an attribute
-
Student Buddy sorts the tasks according to user’s input
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1b. The given index is invalid
-
1ai. Student Buddy returns an error
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
(End of extract)